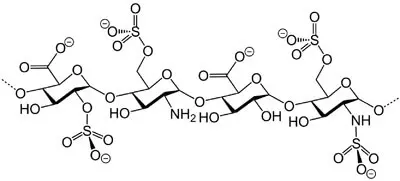
Heparin refers to a group of the body's own unbranched glucosaminoglycans (polysaccharides) that have an inhibitory effect on the blood coagulation cascade. The monomer units of these polysaccharides are glucosamine, glucuronic acid and iduronic acid. In many cases, they carry sulphate groups on the oxygen and nitrogen atoms of the side chains. The molecular weight of heparin is approximately between 4000 and 50000 g/mol. The figure opposite shows a structural section of a heparin molecule.
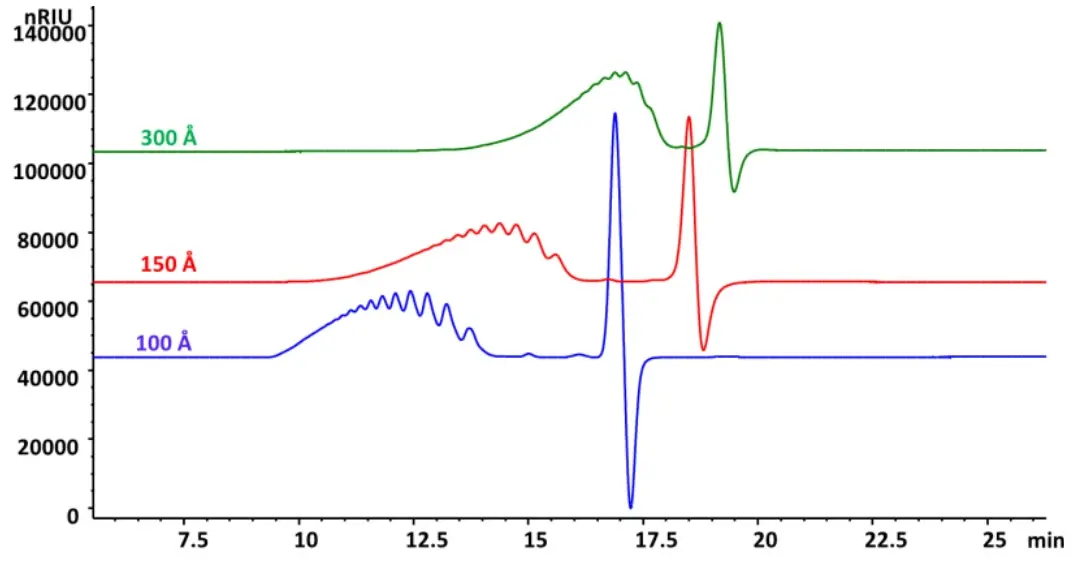
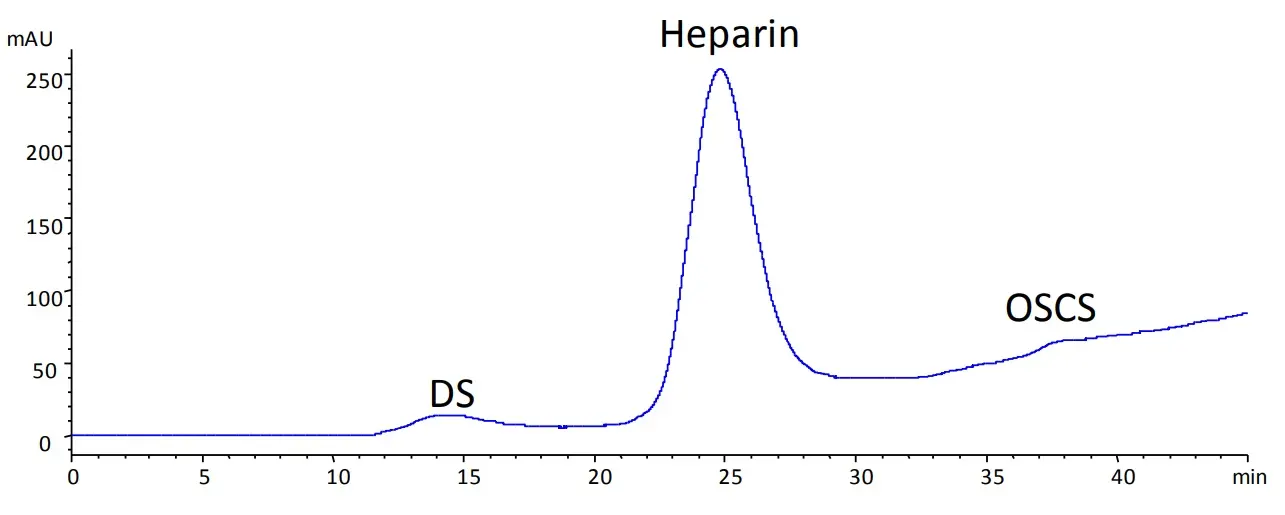
Due to the many functional groups present in the molecule, in particular the negatively charged sulphate or carboxylate groups, heparin is a very polar molecule which exhibits good solubility properties in water. Suitable separation techniques therefore include ion exchange chromatography and gel filtration chromatography (SEC with aqueous eluents). Below you will find some application examples.